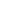
Air Force 1 AF10008A USAF Lockheed-Martin F-35A Lightning II Joint Strike Fighter - Edwards AFB [Low-Vis Scheme] (1:72 Scale)
"The F-35 program executive officer, has stated that the 'F-35 enjoys a significant Combat Loss Exchange Ratio advantage over the current and future air-to-air threats, to include Sukhois, which are currently being flown by the Russian, Indian, and Chinese Air Forces.'"
- Maj Gen Charles R. Davis, USAF, the F-35 program executive officer
 The F-35B is the short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) variant of the aircraft. Similar in size to the A variant, the B sacrifices about a third of the other version's fuel volume to accommodate the vertical flight system. Vertical takeoffs and landings are riskier due to threats such as foreign object damage. Whereas the F-35A is stressed to 9 g, the F-35B is stressed to 7 g. The first test flight of the F-35B was conducted on June 11th, 2008.
The F-35B is the short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) variant of the aircraft. Similar in size to the A variant, the B sacrifices about a third of the other version's fuel volume to accommodate the vertical flight system. Vertical takeoffs and landings are riskier due to threats such as foreign object damage. Whereas the F-35A is stressed to 9 g, the F-35B is stressed to 7 g. The first test flight of the F-35B was conducted on June 11th, 2008.
Unlike other variants, the F-35B has no landing hook. The "STOVL/HOOK" control instead engages conversion between normal and vertical flight. Jet thrust is sent directly downwards during vertical flight; the nozzle is being redesigned to spread the output across an oval rather than circular shape in order to limit damage to asphalt and ship decks. The variant's three-bearing swivel nozzle that directs the full thrust of the engine is moved by a fueldraulic actuator using pressurized fuel.
The United States Marine Corps plans to purchase 340 F-35Bs, to replace current inventories of both the F/A-18 Hornet (A, B, C and D-models), and the AV-8B Harrier II, in the fighter, and attack roles. The Marines plan to use the F-35B from "unimproved surfaces at austere bases" but with "special, high-temperature concrete designed to handle the heat." The USMC intends to declare Initial Operational Capability with about 50 F-35s running interim Block 2B software in the 2014 to 2015 time frame. The USAF had considered replacing the A-10 with the F-35B, but will not do so due to the F-35B inability to generate enough sorties.
The Royal Air Force and Royal Navy plan for the F-35B is to replace the Harrier GR9s, which were retired in 2010. One of the Royal Navy requirements for the F-35B design was a Shipborne Rolling and Vertical Landing (SRVL) mode to increase maximum landing weight to bring back unused ordnance by using wing lift during landing. In October 2010, the UK announced plans to order to the CATOBAR F-35C instead, but in May 2012 the UK reverted to purchasing the F-35B, citing the cost of equipping the UK's new aircraft carriers for the F-35C. In July 2013, Chief of the Air Staff, Air Chief Marshal Sir Stephen Dalton announced that 617 Squadron would be the first operational Royal Air Force squadron to receive the F-35. The second operational squadron will be the Fleet Air Arm's 809 NAS. On June 28th, 2013 the Royal Air Force received three aircraft of the 48 on order, they are currently being based at Eglin Air Force base, and not expected in the UK until 2015. The aircraft are projected to be operational in 2018.
The Italian Navy is preparing Grottaglie Air Station for future operations with the F-35B. The Italian Navy is to receive 22 aircraft between 2014 and 2021, with its Cavour aircraft carrier set to be modified to operate them by 2016. Commandant of the U.S. Marine Corps, General James Amos has said that, in spite of increasing costs and schedule delays, there is no plan B to the F-35B. The F-35B is larger than the aircraft it replaces, which required USS America to be designed without well deck capabilities. In 2011, the USMC and USN signed an agreement that the USMC will purchase 340 F-35B and 80 F-35C fighters while the USN will purchase 260 F-35C fighters. The five squadrons of USMC F-35Cs will be assigned to Navy carriers while F-35Bs will be used on amphibious ships and ashore.
Pictured here is a 1:72 scale replica of a USAF Lockheed-Martin F-35A Lightning II Joint Strike Fighter that was attached to the 461st Flight Test Squadron, 412th Tactical Wing, "Deadly Jesters", then deployed to Edwards AFB,. California.
Now in stock!
Dimensions:
Wingspan: 5-3/4-inches
Length: 8-1/2-inches
Release Date: January 2015
 Historical Account: "Beware Our Sky" - The 461st Flight Test Squadron is a United States Air Force squadron, assigned to the 412th Operations Group of Air Force Materiel Command, and is stationed at Edwards Air Force Base, California. The It performs flight testing on the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II.
Historical Account: "Beware Our Sky" - The 461st Flight Test Squadron is a United States Air Force squadron, assigned to the 412th Operations Group of Air Force Materiel Command, and is stationed at Edwards Air Force Base, California. The It performs flight testing on the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II.
The squadron's origins can be traced to the 361st Fighter Squadron, which flew combat in the European Theater of Operations, where it won a Distinguished Unit Citation before inactivating in 1945.
In 1985, the 361st Squadron was consolidated with the 461st Tactical Fighter Training Squadron. The 461st had been activated in 1956 as the 461st Fighter-Day Squadron and served as a fighter unit in Europe until 1959. It served as a training unit in Arizona starting in 1977. The consolidated unit was inactivated in 1994, but was activated again in its current role in 2006.